Signalment, clinical features, echocardiographic findings, and outcome of dogs and cats with ventricular septal defects: 109 cases (1992–2013)
AVSD consists of an opening in the IVS resulting from incomplete development or misalignment of the IVS during the embryonic period.1,2 Several VSD types have been defined according to the location of the defect within the IVS.
Supracristal VSDs (also known as conoseptal, subarterial, or infundibular VSDs) are found below the right and noncoronary aortic valve cusps in conal or outlet regions of the IVS. Conversely, membranous VSDs are located within the membranous portion of the IVS just below the aortic valve cusps. If the defect extends to the dorsal part of the muscular portion of the IVS, VSDs are described as perimembranous, paramembranous, or conoventricular (the 2 latter terms being more appropriate).3–5 Muscular VSDs are entirely enclosed in the muscular IVS and may involve the inlet, outlet, or trabecular parts of the IVS.3 Lastly, a fourth form of VSD is also described: atrioventricular canal type VSDs (involving the inlet of the right IVS portion immediately beneath the atrioventricular valve apparatus). Additionally, VSDs may be isolated, multiple, or concomitant with other CHDs. Isolated VSDs, regardless of the type, usually result in a left-to-right shunting across the defect, and both the magnitude of the shunting flow and its cardiac consequences are mainly determined by the size of the defect and also pulmonary vascular resistances.
Ventricular septal defects have been extensively studied in people and they are considered the most common human CHD, representing 324 of 1,000 (32.4%) to 1,492 of 2,867 (52.0%) of all CHDs in several studies.6–11 Conversely, VSDs seem to be less common in dogs, accounting for 17 of 276 (6.2%) to 20 of 162 (12.3%) of CHDs in this species,12–19 and the reported proportion of VSDs in cats is variable, ranging from 13 of 107 (12.1%) to 27 of 48 (56%) of CHDs according to different sources.12,13,16,20,21
Ventricular septal defects in dogs and cats have mainly been studied in the context of retrospective reviews of CHDs.12–14,17–22 Data from large populations of animals affected by VSDs are therefore lacking, and to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the comparative survival time and prognostic factors predictive of survival in dogs and cats with VSDs remain unknown.
The aims of the study reported here were to investigate the signalment and clinical and echocardiographic features of dogs and cats with VSDs and to assess the long-term clinical outcome of affected animals, including survival rates for animals with isolated VSDs.
Materials and Methods
Criteria for selection of cases
Hard copy and electronic medical records for client-owned dogs and cats that underwent conventional (ie, M-mode and 2-D) echocardiographic and standard Doppler echocardiographic examination, leading to the diagnosis of VSD, at the Cardiology Unit of Alfort, National Veterinary School of Alfort, Maisons-Alfort, France, and at the Centre Hospitalier Vétérinaire des Cordeliers, Meaux, France, between October 1, 1992, and October 31, 2013 were evaluated. Dogs and cats with isolated or nonisolated VSDs confirmed by color flow Doppler echocardiography were included in the study. Animals with equivocal Doppler echocardiography results or for which color flow Doppler mode was not used to confirm a VSD were excluded.
Medical records review
Species, breed, age, sex, and body weight were obtained from the medical records. Clinical status at the time of diagnosis, echocardiographic findings (including presence and type of concomitant CHD, if applicable) and measurements, and any outcome data included in the record were also recorded.
Standard and Doppler echocardiographic examinations
Standard 2-D, M-mode, and Doppler examinations were performed in awake standing animals with continuous ECG monitoring by trained observers using ultrasonography unitsa–e as previously described.23,24 Transverse diameters of the aorta and the left atrium were measured in late diastole with a 2-D method by use of the right parasternal short-axis view at the level of the aortic valve, and the left atrial-to-aortic diameter ratio was calculated as described elsewhere.25 Presence of VSD was assessed on right parasternal long-axis 4- or 5-chamber views and by examination of the IVS on right or left long-axis, short-axis, or oblique views.26,27 Transverse views of the heart base, just proximal to the pulmonic valve within the right ventricular outflow tract, were also examined.26,27 Color flow Doppler mode was used to visualize and confirm the presence of VSD. Both color flow and continuous-wave Doppler modes were used to assess the shunt direction (left-to-right, right-to-left, or bidirectional), as previously described.27–29 Continuous-wave Doppler mode was also used to measure the maximal velocity through the defect. The maximal size of the defect (ie, VSD diameter), which may vary according to the phases of the cardiac cycle, was measured from Doppler color flow map echocardiograms at the level of the defect through the IVS (Figure 1).27 Color flow Doppler images were analyzed frame by frame to compute the maximum area of the VSD jet signal, and the largest color flow VSD diameter was then measured.
The VSD:Ao was then calculated. Aortic regurgitation, when present, was classified as mild if the jet width was < 25% of the dimension of the left ventricular outflow tract (jet width ratio) on the right parasternal 5-chamber view and as moderate or severe if the jet width ratio was between 25% and 65% or > 65%, respectively, in color flow Doppler mode.30 Aortic cusp prolapse assessed with the 2-D mode was noted as present or absent. The Qp:Qs, which represents the magnitude of left-to-right shunting, was assessed by combining 2-D echocardiography and pulsed-wave Doppler mode data as previously described (ie, pulmonary and systemic flow rates were obtained by multiplying crosssectional areas of the pulmonary trunk and aortic root, with the velocity-time integrals of pulmonary and aortic flows, respectively).9,26,31 Ventricular septal defects were considered as small (restrictive), moderate (moderately restrictive), or large (nonrestrictive) if Qp:Qs was < 1.5, between 1.5 and 2.5, and > 2.5, respectively.32,33 Concomitant CHDs were also recorded.
Classification of VSD
Ventricular septal defects were classified on the basis of echocardiographic findings as isolated (ie, solitary lesions) or nonisolated (with ≥ 1 other CHD present). They were also divided into 4 types according to their localization and anatomic features.3,5,7,33–37 Type 1 VSDs were supracristal, type 2 VSDs were membranous or perimembranous, and type 3 and 4 VSDs were atrioventricular canal type and muscular VSDs, respectively.
Clinical status
At the time of diagnosis, animals were classified as either clinically or subclinically affected (ie, with or without clinical signs attributed to VSD, such as exercise intolerance, signs of congestive heart failure, syncope, and cyanosis, respectively). Exercise intolerance was defined as a decreased capacity of usual daily exercise as noted by the owners.
Follow-up
Follow-up was based on a review of the patient’s records and was performed for animals with isolated VSDs only. Owners of animals for which the outcome could not be found in the database were contacted by telephone, mail, or email to determine the current status of their animals: alive (clinically or subclinically affected) or dead (date and cause of death, if known). Animals that were subclinically affected at the time of diagnosis were considered as stable (or nondecompensated) if they remained subclinically affected at the time of last follow-up or as decompensated if they had developed ≥ 1 of the clinical signs attributed to VSD. Animals for which the outcome could not be obtained were considered lost to follow-up and were consequently censored at the time of their last examination.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by computer software.f Data were expressed as proportion, percentage, or median and range and compared among groups by the log rank test. Survival curves were determined by the Kaplan-Meier method. Variables of interest were compared between groups (species [dog vs cat] and clinical sign [present vs absent] subgroups) by means of a Mann-Whitney test. Correlations between VSD diameter or VSD:Ao and echocardiographic variables of interest were assessed by means of the Spearman rank test. Values of P ≤ 0.05 were considered significant.


Figure 1—Representative color flow Doppler mode echocardiograms used to visualize the VSD and measure the maximal VSD size (ie, VSD diameter) in a cat (A) and a dog (B).
A—Right parasternal 5-chamber view showing a left-to-right shunt through a moderate perimembranous VSD, represented by an aliased turbulent flow accelerating in the left ventricular outflow tract just below the aortic valve into the right ventricle across the defect. Measurement of the VSD diameter is shown by the double-headed arrow.
B—Visualization of a left-to-right shunt through a small supracristal VSD and measurement of the maximal diameter of the defect (double-headed arrow) on the right parasternal shortaxis view at the level of the aortic valve. Scales on the left side of each image represent distance to the transducer (in cm).
Ao = Aorta. LA = Left atrium. LV = Left ventricle. PT = Pulmonary trunk. RV = Right ventricle. RVOT = Right ventricular outflow tract.
Results
Dogs and cats with VSD
The study population consisted of 109 animals (56 dogs and 53 cats) with a diagnosis of VSD. Of these, 88 were evaluated at the Cardiology Unit of Alfort and 21 at the Centre Hospitalier Vétérinaire des Cordeliers. The 56 dogs represented 30 breeds, including French Bulldog (8 [14%]); Fox Terrier (4 [7%]); Jack Russell Terrier, English Bulldog, Cocker Spaniel, and mixed (3 [5%] each); and Poodle, Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, German Shepherd Dog, Maltese, Collie, West Highland White Terrier, Yorkshire Terrier, and Border Terrier (2 [4%] each). Sixteen other breeds, including 5 of terrier type, comprised < 2% of the canine population.
There were 34 male and 22 female dogs; median age at the time of VSD diagnosis was 9 months (range, 2.2 months to 11.8 years), and median weight was 8 kg (17.6 lb; range, 1 to 60 kg [2.2 to 132 lb]). The 53 cats comprised 9 breeds, including domestic shorthair (35 [66%]), Maine Coon (6 [11%]), Norwegian Forest Cat and Sphynx (3 [6%] each), and Persian (2 [4%]). Less than 2% of the cats were of other breeds. There were 27 male and 26 female cats. Median age was 1 year (range, 1.5 months to 12.7 years), and median weight was 3.8 kg (8.4 lb; range, 0.9 to 7.7 kg [2.0 to 17.0 lb]).
VSD types and concomitant CHDs
An isolated VSD was diagnosed in 53 of 109 (48.6%) animals, including 26 of 56 (46%) dogs and 27 of 53 (51%) cats. Of the remaining 56 animals, tetralogy of Fallot was diagnosed in 20 (36%; 10/30 [33%] dogs and 10/26 [38%] cats). Among patients with tetralogy of Fallot were 1 dog with 4 concomitant CHDs (aortic stenosis, ASD, persistent left cranial vena cava, and an abnormal right coronary artery) and 2 cats with 2 concomitant CHDs each (1 with mitral valve dysplasia and ASD, and 1 with mitral and tricuspid valve dysplasia). Other cases of VSD with pulmonic stenosis included 5 of 56 (9%) dogs, 1 of which also had mitral valve dysplasia. In total, VSD with pulmonic stenosis with and without other CHDs comprised 25 of 56 (45%) VSD associations.
In the remaining 15 dogs and 16 cats, VSDs were found in various combinations with ≥ 1 of the following conditions: mitral valve dysplasia (7 dogs and 9 cats), ASD (4 dogs and 3 cats), aortic stenosis (4 dogs and 3 cats), tricuspid valve dysplasia (2 dogs and 4 cats), persistent left cranial vena cava (2 dogs and 2 cats), persistent truncus arteriosus (1 dog and 1 cat), quadricuspid aorta (2 dogs), and mitral valve stenosis (1 cat).
Two-dimensional and color flow Doppler mode echocardiography revealed that the most common VSDs in the study population were type 2 (membranous and perimembranous). These were identified in 82 of 109 (75.2%) animals, including 40 of 56 dogs (15 and 25 with isolated and nonisolated VSDs, respectively) and 42 of 53 cats (22 and 20 with isolated and nonisolated VSDs, respectively). Type 1 (supracristal) VSDs were the next most common, identified in 22 of 109 (20.2%) animals (15 dogs [10 with isolated and 5 with nonisolated VSDs] and 7 cats [4 with isolated and 3 with nonisolated VSDs]). Only 3 animals (1 dog and 2 cats) had type 3 (atrioventricular canal type) VSDs, and only 2 (both cats) had type 4 (muscular) VSDs.
Clinical findings in animals with isolated VSDs
At the time of diagnosis, a systolic heart murmur heard best at the right sternal border (median grade 4/6; range, 3/6 to 5/6) was detected in all animals with isolated VSDs (n = 53 [26 dogs and 27 cats]). Forty-three of 53 (81%) patients were subclinically affected at the time of diagnosis. The remaining 10 animals (19%; 4 dogs and 6 cats) had ≥ 1 clinical sign. These included respiratory signs, such as dyspnea (n = 8 [2 dogs and 6 cats]); cough (3 [2 dogs and 1 cat]); and thoracoabdominal asynchrony (also called paradoxical breathing38), characterized by increased inspiratory effort resulting in sunken flanks when the thorax expands and bulging flanks when the thorax is depressed (2 cats, both with pleural effusion). Cyanosis was detected in 1 dog, and exercise intolerance was reported for 2 dogs. Congestive heart failure (evidenced by pulmonary edema or pleural effusion) was detected in 4 of the 10 clinically affected animals (3 cats and 1 dog).
Treatment status at the time of diagnosis was known for all 53 animals with isolated VSDs: 44 (83% [21 dogs and 23 cats]) were untreated, and 9 (17% [5 dogs and 4 cats]) were receiving ≥ 1 of the following drugs: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (eg, benazepril, enalapril, imidapril, or ramipril; 6/53 [11%]; 4 dogs and 2 cats), furosemide (2/53 [4%]; 1 dog and 1 cat), spironolactone (4/53 [8%]; 3 dogs and 1 cat), altizide (2/53 [4%]; both dogs), and diltiazem (1/53 [2%]; a cat).
Conventional and standard Doppler echocardiographic findings at diagnosis
Some quantitative data were not available for all animals. Data regarding VSD diameter, assessed by color flow Doppler mode, were available for 46 of 53 (87%) animals (21 dogs and 25 cats) with a diagnosis of isolated VSD. Median VSD diameter was 3.9 mm (range, 1.4 to 12 mm) for dogs and 3.5 mm (range, 1 to 12 mm) for cats. The VSD:Ao was calculated for 42 of the 53 animals (79%; 20 dogs and 22 cats); median values were 0.23 (range, 0.08 to 0.57) and 0.32 (range, 0.16 to 1.30) for dogs and cats, respectively.
Direction and velocity of the shunt
The direction of the shunt, assessed by means of combined color flow and continuous-wave Doppler modes, was left-to-right for 51 of 53 (96%) animals with isolated VSD, and right-to-left (consistent with an Eisenmenger complex) for the remaining 2 (4%). The 2 patients with right-to-left shunt were a dog with a VSD diameter of 7.4 mm and VSD:Ao of 0.45 and a kitten with a VSD diameter of 7.8 mm and VSD:Ao of 1.30. Maximal flow velocity through the defect, calculated in the continuous-wave Doppler mode for left-to-right shunts, was available for 37 animals. Median maximum flow velocity was 5.13 m/s (range, 0.57 to 6.75 m/s) for all animals (n = 37), 5.13 m/s (range, 3 to 6.75 m/s) for dogs (19), and 4.86 m/s (range, 0.57 to 6.72 m/s) for cats (18). Most (28/37 [76%]) patients had maximum flow velocity between 4.8 and 6.75 m/s.
Qp:Qs
Pulmonary-to-systemic flow ratio was calculated for 32 of 53 (60%) animals with isolated VSDs, all with left-to-right shunts. The median Qp:Qs was 1.2 (range, 0.83 to 2.70) for 17 dogs and 1.35 (range, 0.76 to 2.48) for 15 cats. The Qp:Qs was < 1.5 for 24 of 32 (75%) animals (12 dogs and 12 cats), 1.5 to 2.5 for 6 (19%) animals (3 dogs and 3 cats), and > 2.5 for 2 (6%) animals (both dogs).
Aortic regurgitation and aortic cusp prolapse
Aortic regurgitation was present in 19 of 53 (36%) animals (15 dogs and 4 cats) with isolated VSDs and was considered mild for 12 animals (9 dogs and 3 cats), moderate in 3 (2 dogs and 1 cat), and severe in 4 (all dogs). Nine of the 19 animals with aortic regurgitation had type 1 VSDs, and the other 10 had type 2 VSDs. Aortic cusp prolapse was identified only in dogs with type 1 VSD (n = 3) and was associated with moderate and severe aortic regurgitation in 1 and 2 dogs, respectively.
Correlation of Qp:Qs with VSD diameter and VSD:Ao
The Qp:Qs was significantly correlated with VSD diameter whether evaluated in the population of study animals for which data were available (n = 32; r = 0.579; P < 0.001), in dogs (17; r = 0.529; P = 0.028), or in cats (15; r = 0.713; P = 0.002). The Qp:Qs was also significantly correlated with VSD:Ao in the study population for which data were available (n = 32; r = 0.702; P < 0.001), in dogs (17; r = 0.689; P = 0.002), and in cats (15; r = 0.829; P < 0.001). The strongest correlations were found for the VSD:Ao (Figure 2).
Associations among echocardiographic variables and clinical signs
Data regarding both VSD diameter and presence or absence of clinical signs were available for 46 of 53 animals with isolated VSDs (10 clinically affected and 36 with subclinical disease). Dogs with clinical signs attributed to VSD (n = 4) had a significantly (P = 0.039) greater VSD diameter (median, 5.8 mm; range, 4.1 to 12.0 mm) than did subclinically affected dogs (17; median, 3.3 mm; range, 1.4 to 8.4 mm). However, VSD diameter did not differ significantly (P = 0.258) between cats with (n = 6; median, 4.3 mm; range, 1.6 to 12.0 mm) and without (19; median, 2.7 mm; range, 1.0 to 7.5 mm) clinical signs attributed to VSD.
Data for VSD:Ao, together with the presence or absence of clinical signs, were available for 42 of the 53 animals (8 and 34 clinically and subclinically affected, respectively). Results were similar to those found for VSD diameter; the VSD:Ao was significantly (P = 0.02) greater in dogs with (n = 4; median, 0.36; range, 0.23 to 0.57) than in dogs without (16; median, 0.22; range, 0.08 to 0.45) clinical signs attributed to VSD. In cats, the VSD:Ao did not differ significantly (P = 0.726) between clinically (n = 4; median, 0.3; range, 0.19 to 1.3) and subclinically affected (18; median, 0.32; range, 0.16 to 0.96) animals.
Data regarding Qp:Qs and the presence or absence of clinical signs were available for 32 of the 53 animals (5 clinically affected and 27 subclinically affected). The Qp:Qs was significantly (P = 0.02) greater in clinically affected (median, 2.17; range, 1.27 to 2.7) than subclinically affected (median, 1.2; range, 0.76 to 2.48) animals. The Qp:Qs was also significantly (P = 0.004) greater in dogs with (n = 4; median, 2.35; range, 1.7 to 2.7) than in dogs without (13; median, 1.11; range, 0.83 to 1.61) clinical signs attributed to VSD. Differences between clinically and subclinically affected cats were not calculated because only 1 cat (Qp:Qs, 1.27) was clinically affected (vs 14 subclinically affected cats; median, 1.37; range, 0.76 to 2.48).
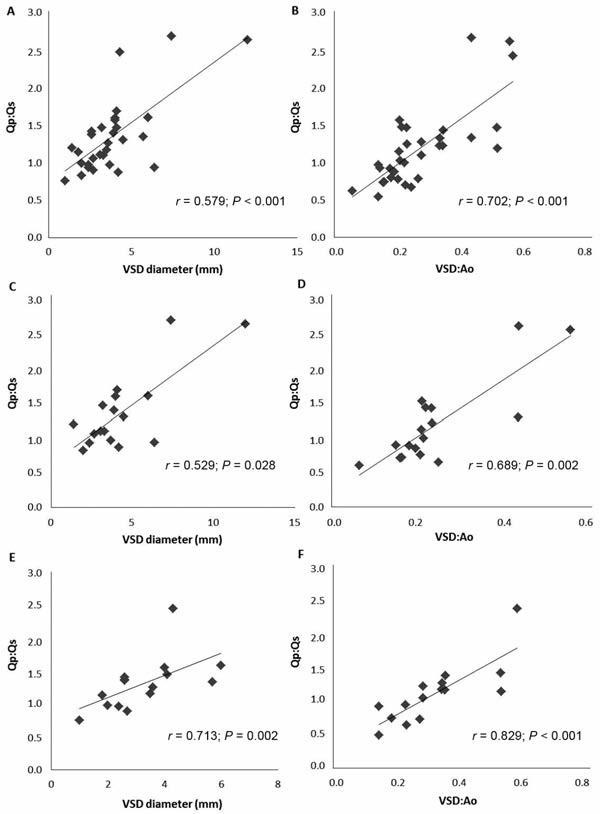
Figure 2—Correlations of Qp:Qs with VSD diameter and VSD:Ao in 32 of 53 study animals with isolated VSDs for which data were available (A and B) and in subpopulations of dogs (C and D; 17/32) and cats (E and F; 15/32).
Development of clinical signs and survival time
One dog with an isolated large VSD (12 mm in diameter; Qp:Qs, 2.65) underwent a successful surgical closure of the defect (by means of an open beating heart surgical technique with cardiopulmonary bypass) and was therefore excluded from subsequent statistical analyses. The dog was reportedly doing well 8 years after VSD closure, with no recurrence of the previous clinical signs (exercise intolerance) attributed to VSD before surgery.
Follow-up data were available for 37 of the remaining 52 animals with an isolated VSD (16 dogs and 21 cats). Twenty-nine of the 37 animals were subclinically affected and 8 were clinically affected at the time of diagnosis. None of the 29 subclinically affected animals with follow-up data available developed clinical signs attributable to VSD after the initial examination.
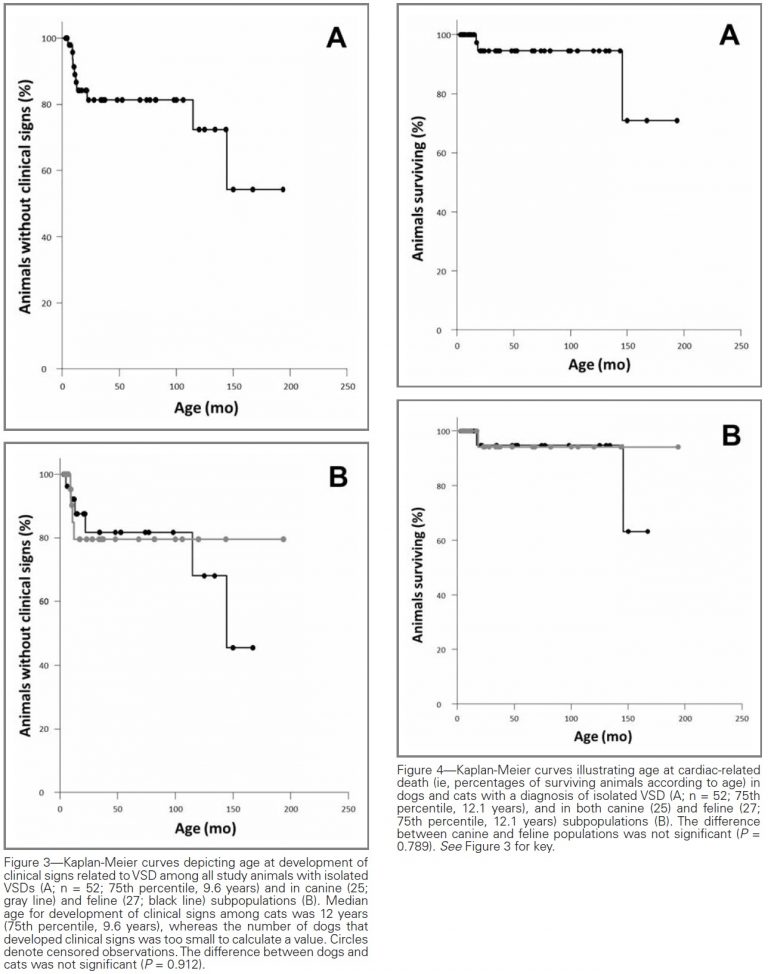
Owing to the high proportion of dogs with isolated VSD that remained subclinically affected at the end of the study period (13/16), median age at development of clinical signs could not be calculated in this species, whereas median age for this finding in cats was 12 years (Figure 3).
Death from any cause was reported for 13 of 37 animals (6 dogs and 7 cats) at a median age of 12 years. The median age was 12 years for dogs and 12.1 years for cats, with no significant (P = 0.979) difference between the 2 groups.
Cardiac death related to left-sided congestive heart failure was only reported for 3 animals (2 cats at 1.4 and 12.1 years of age and 1 dog at 1.5 years of age); these were among the 8 animals clinically affected at the time of diagnosis for which follow-up data were available. Of these 3, cardiac-related death of only 1 cat was considered strictly related to VSD, because the dog and the remaining cat had developed severe acquired heart disease at adult age (dilated cardiomyopathy and degenerative mitral valve disease, respectively). The cat with VSD-related death had a large type 3 VSD (12 mm in diameter; Qp:Qs data unavailable) with a left-to-right shunt at the time of diagnosis.
Of the remaining 5 animals (2 dogs and 3 cats) that were clinically affected at the time of VSD diagnosis and had follow-up data available, the evaluation and diagnosis of VSD were considered recent (occurring 0.9 and 2.4 years before the end of the study) for 4. Diagnosis for the remaining animal, a dog, was made approximately 4 years before the end of the study. Medical treatment was ongoing for 3 of these 5 animals (2 dogs and 1 cat with left-to-right shunts). The 2 dogs were receiving benazepril as well as spironolactone and altizide, and the cat was receiving benazepril and furosemide. The 2 untreated animals included a cat that was 10.8 years old at the end of the study (with a diagnosis of type 1 VSD at 9.6 years of age) and a cat that was 1.7 years old at the end of the study (with a diagnosis of a type 2 VSD [7.8 mm in diameter; Qp:Qs data unavailable] at 9.2 months of age). The older cat had a left-to-right shunt and VSD:Ao of 0.38, and the younger cat had a right-to-left shunt with a VSD:Ao of 1.3.
Median time to cardiac-related death in the 2 species subgroups could not be calculated, because of the high proportion of animals with isolated VSDs that did not have death attributable to cardiac disease (Figure 4). Age at development of clinical signs attributed to VSD (P = 0.989) and age at death from all causes (P = 0.366) or from cardiac causes (P = 0.748) were not associated with the presence or absence of aortic regurgitation.