Clinical application of the left ventricular flow propagation velocity with Color M-mode Doppler in 26 dogs with mitral valve disease
Echocardiography is currently an obligate tool when studying cardiac diseases and their consequences in domestic carnivores. This test allows the identification of anatomic, morphologic (valvular, myocardial, large vessels) and hemodynamic (blood flows) abnormalities seen with cardiac diseases. Several modes of data acquisition are available for this purpose: 2D and M-mode imaging, conventional Doppler and more recently tissue Doppler Imaging (tDI) 1-3.
Logical assessment of some abnormalities gives an idea of myocardial performance and functioning. Ventricular function is composed of a diastolic phase and a systolic phase. Echocardiographic measurement indices (either measured or calculated) are already available for each phase taken separately or together. These indices are diverse and can be obtained with the echocardiographic modes described previously 4, 5. Transmitral flow with a pulsed-wave Doppler mode is most commonly used in general practice for evaluation of diastolic function 6-8.
Transmitral flow is composed of an early-diastole E wave (passive ventricular filling), and an end-diastole A wave (active ventricular filling, associated with atrial contraction). In the normal dog the mitral E/A ratio varies between 1.04 and 2.42 9.
Three main abnormal flow profiles are recognized 10-12: type 1 profile, where ventricular relaxation is impaired when the filling pressures during end-diastole are reduced (“abnormal relaxation”); type 2 profile, also called restrictive where ventricular compliance is impaired and filling pressures are very high during end-diastole (“restrictive”); type 3 profile, where the relaxation is impaired and filling pressures are moderately high during end-diastole (“pseudonormal”). Even though these mitral indices are easy to obtain and therefore appealing, their use is however limited because they combine ventricular relaxation and loading conditions in evaluating diastolic function 13, 14. Moreover, these indices can vary, depending on the heart rate 13, 14.
It is therefore sometimes difficult to estimate the diagnostic value of some abnormalities because their origin can be multifactorial, for example when a type 3 flow (“pseudo-normal”) is identical to a normal flow 13-15.
Other indices for evaluation of diastolic function have been studied in domestic carnivores. Left ventricular flow propagation velocity (Vp) can be obtained by pulsed-wave Color M-mode Doppler imaging and is a new index of diastolic function 16 that has been experimentally validated in healthy dogs and cats 17, 18.
Unlike with transmitral flows, this velocity does not depend on loading conditions and heart rate 19, 20, but only on ventricular relaxation19, 20. When combined with mitral E wave velocity (pulse-wave Doppler), the E/Vp ratio can be obtained which does not depend on ventricular relaxation, but only on loading conditions 21, 22.
Measurement of Vp allows the establishment of an independent index of ventricular relaxation, and its ratio with the E wave provides an independent index which reflects end diastole filling pressures. This measure has been experimentally validated in the normal dog. The purpose of this study was to investigate the use of Vp and E/Vp as indices of evaluation of diastolic function and filling pressures in the dog with MVD.
Our first hypothesis was that Vp would be significatively different between healthy dogs and dogs with relaxation abnormalities, when comparing the different Appleton flows, allowing a distinction between a normal profile (healthy dog) and a type 3 “pseudonormal” profile. Our second hypothesis was that it is possible to use the ratio E/Vp for the evaluation of filling pressures during end-diastole, in contrast to Appleton profiles.
Materials and methods
The animals were presented to the Cardiology Service by their owners. One group of dogs was healthy, with no morphologic or hemodynamic cardiac abnormalities; the other groups of dogs suffered from acquired MVD with mitral insufficiency which had not yet been treated at that time. The diagnosis of cardiac failure was made based on clinical signs according to ISACHC classification criteria 23, or if thoracic radiographs showed evidence of congestive heart failure.
The dogs were divided in four groups:
- group 1: normal dogs (control group) (normal stage) ;
- group 2: dogs with MVD and a type 1 mitral profile (abnormal relaxation) (stage 1) ;
- group 3: dogs with MVD and a type 3 mitral profile (pseudonormal) (stage 3) ;
- group 4: dogs with MVD and a type 2 mitral profile (restrictive filling) (stage 2) ;
Dogs with a disease other than cardiac in origin, or with a concomitant disease were not included in the study. Dogs with a cardiac disease other than MVD, or dogs MVD undergoing treatment (that could influence and alter echocardiographic results) and dogs presented on an emergency basis were excluded from the study.
The Tukey test was performed between groups to test for differences regarding age, weight, heart rate (HR) and shortening fraction (SF). A linear correlation was performed to test relation between age, weight, HR and SF and Vp and E/Vp. For each parameter (E, A, Vp and E/Vp), 5 successive measures were taken on 5 consecutive cardiac cycles.
Mean and standard deviation were calculated. For each parameter (E, A, Vp and E/Vp), mean, standard deviation, median, maximum and minimum values were calculated for each group. For each group, Vp and E/Vp distribution were compared with non parametric tests because the small number of animals in each group was not representative of a normal distribution.
Therefore an ANOVA on ranks procedure using the Dunn test was performed to test for differences between groups. A value of p < 0.05 (2-sided) was considered significant. Results are expressed in mean (median) ± standard deviation.
The transmitral valve flow profile was obtained with left parasternal imaging using an apical four-chamber long axis view with pulsed-wave conventional Doppler. The sample volume was positioned just below the mitral annulus. E wave and A wave were measured in m/s.
The different mitral types (1, 2 and 3) corresponded to those described before 10-12 :
- type 1: small E wave, large A wave, increase in the deceleration time of E wave, ratio E/A < 1 ;
- type 2: large E wave, small A wave, decreased deceleration time, ratio E/A increased (> 2.42) 9 ;
- type 3: E and A waves of normal magnitude, normal deceleration time, ratio E/A within normal limits (between 1.04 and 2.42) 9.
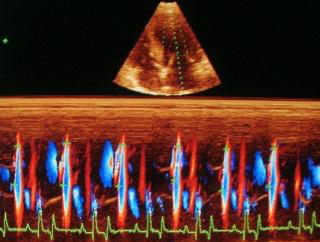
The left ventricular flow propagation velocity (Vp) was obtained with a Color M-mode pulsed-waved Doppler with a left apical long axis image, four chamber view. From this image, and with two-dimensional echocardiography, the color box was positioned in order to sample the entire surface of the left ventricle, from the mitral annulus to the apex 20.
Aliasing was programmed to be between 50 % and 75 % of the maximal velocity of the E wave of the transmitral flow 20. The M-mode cursor was then positioned in the continuity of the ventricular color flow during diastole. The M mode was then activated with a maximum sweep speed (50 mm/s).
Vp was measured as the slope during the first aliasing of E wave from the mitral annulus to the apex of the left ventricle. It was measured in m/s. For each parameter (E, A, Vp, ratio E/Vp), 5 successive measures were taken on 5 consecutive cardiac cycles. Mean and standard deviation were then calculated.
Results
- 26 dogs were included in the study:
- group 1: normal dogs (control group): 5 dogs ;
- group 2: dogs with MVD and abnormal relaxation mitral profile: 7 dogs ;
- group 3: dogs with MVD and pseudonormal mitral profile: 8 dogs ;
- group 4: dogs with mitral MVD and restrictive mitral profile: 6 dogs.
- There were 12 females and 14 males. The mean age was 8.5 ± 3.3 years.
- The age of the dogs in group 4 was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than group 1.
- There were no differences between the other groups regarding age and no differences between all groups regarding weight.
- Dogs of group 4 attended to have higher ISACHC class than the other groups.
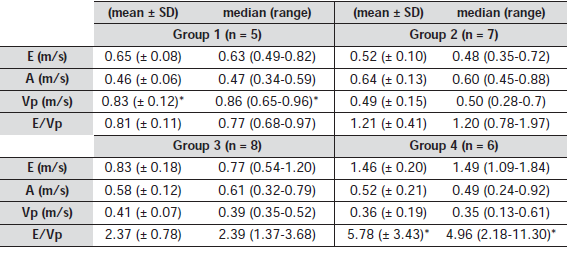
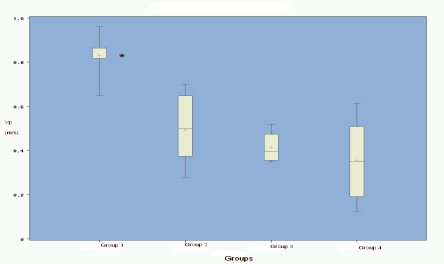
There was a significant difference for Vp between group 1 (normal dogs) and groups 2-4 (dogs with MVD) (p < 0.05). There was no difference between the different groups of dogs with MVD (group 2-4). There was no significant correlation between age, weight, HR or SF and Vp.
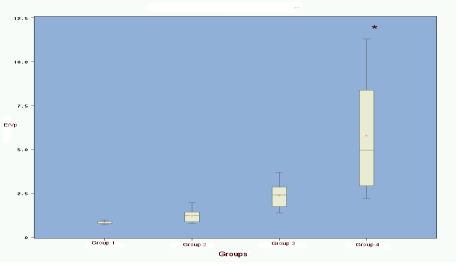 There was a significant difference for E/Vp between group 4 (restrictive profile) and group 1 (normal dogs), group 2 (abnormal relaxation), and group 3 (pseudonormal) (p < 0.05). There was no difference between groups 1, 2 and 3. There is no significant correlation between age, weight, HR or SF and E/Vp.
There was a significant difference for E/Vp between group 4 (restrictive profile) and group 1 (normal dogs), group 2 (abnormal relaxation), and group 3 (pseudonormal) (p < 0.05). There was no difference between groups 1, 2 and 3. There is no significant correlation between age, weight, HR or SF and E/Vp.